Introduction
In this blog post I will describe how you can transition to Windows Update for Business from a legacy WSUS environment.
It is easy to just set it up “modern management” so to speak but managing legacy systems and make sure every system works and get its updates from a certain source is another ballgame, trust me.

Questions like:
How does dual scan work?
What systems are supported?
Which device groups need to be involved?
What order should you go modern?
Do you allow telemetry?
Etc.
First, we need to setup co-management, then we can play around moving workloads and use cloud features.
This is what I will manage during my transition:
|
Component |
Source |
|
Windows Quality Updates |
Windows Update for Business |
|
Windows Feature Updates |
Windows Update for Business |
|
Office 365 |
Configuration Manager |
|
3rd party updates |
Configuration Manager |
|
Drivers |
Configuration Manager |
|
Microsoft Product Updates |
Configuration Manager |
Hopefully some day in the future we will have more options than Monthly enterprise channel in the Office health center, and then it will be time for transition Office 365 patching.
Requirements
- License. (Intune license on the administrator account setting up Co-Management.)
- Configuration Manager version 1710 or later.
- If using Autopilot for provisioning clients, CMG is required.
- Device must be connected to Azure AD, Hybrid Azure-AD joined, or Azure-AD joined only.
- Intune configured
- Windows 10 1709 or later
- Enable co-management in Configuration Manager
- Global Azure AD Administrator
- Full administrator in Configuration Manager on ALL scopes
- Windows 10 Pro, Enterprise, Pro for Workstation, and Education editions.
- The device must be running Windows 10 version 1703 or later (to configure Windows 10 feature updates)
- The device must have telemetry turned on, with a minimum setting of Basic.
- If you are enrolling large scale, Intune enrollment without user interaction requires Azure AD Premium.
Co-management license requirements. (Thanks Ben for pointing that out! Go follow this dude he has amazing content)
While some of the benefits by going co-managed devices is leveraging Conditional access, that will be part of the journey too, but not covered in this post. Lots of good resources on the topic already exists.
Paths towards Windows Update for Business:
- Group policy management
- Mobile Device Management (MDM) – Intune (preferred)
Setup the environment
Before setting up anything, you should analyze what settings you have put on to your systems. Eg. did you setup WSUS using GPO? or other settings for windows update?
Then you need to take that into consideration before proceeding, as it is important to know that deviating settings, can result in unwanted user experience. (Thanks Adam for pointing that out! Go follow Adam, he really have great tweets and does have daily operations with this stuff)
Open your configuration manager console
Navigate to Administration -> overview -> Client Settings
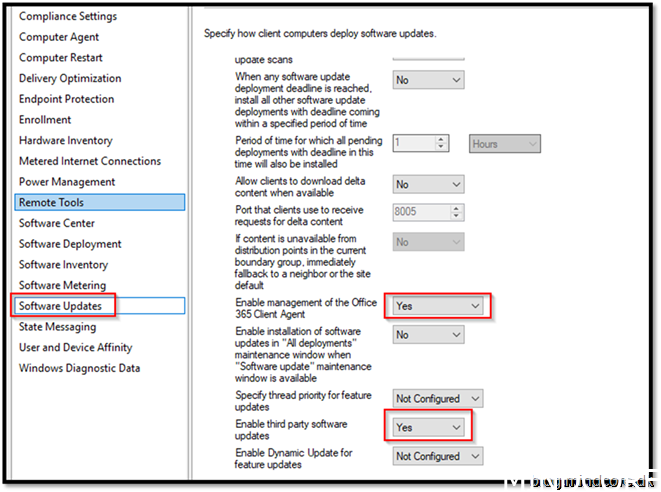
These settings will make sure our devices know where to get its content when it comes to Office365 and Third-party software updates.
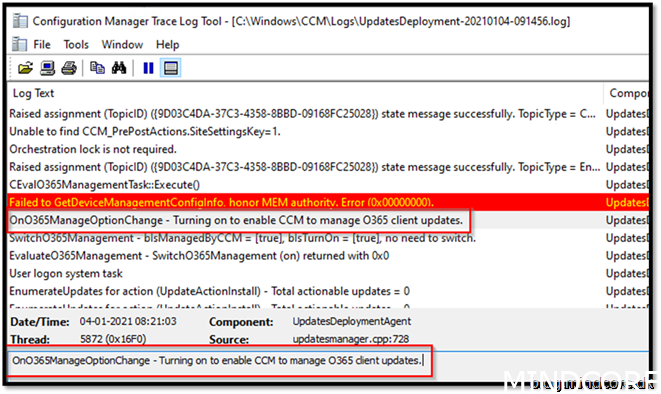
When applied UpdatesDeployment log on your clients should write something like this:
Go to assets and compliance
Create a new folder
Name it with a given naming standard
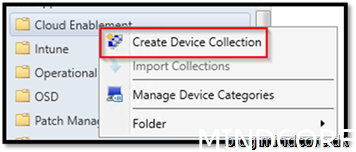
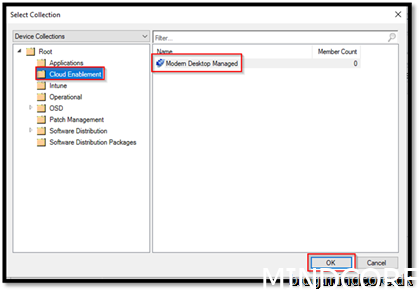
Create Device Collection in the folder Cloud Enablement
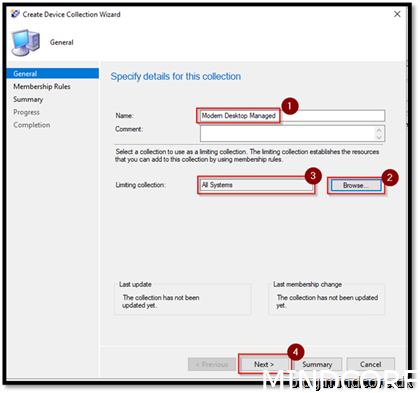
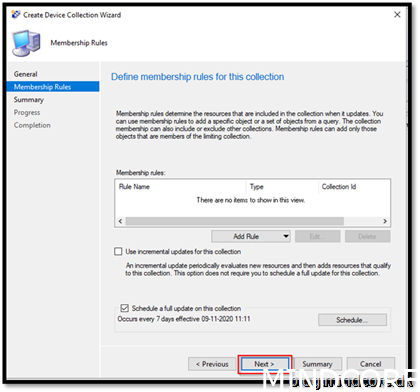
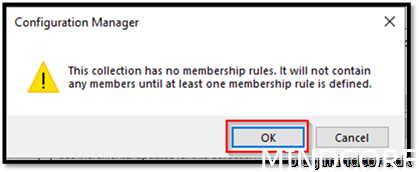
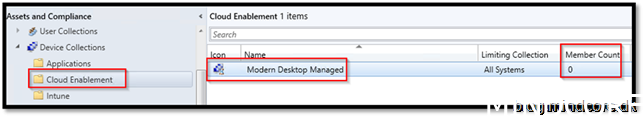
We created the collection where we add devices that should enroll themselves to Intune.
We need to create collections for the separate workloads
Create 7 collections with the names:
Modern Desktop Managed Workload Staging – Compliance Policies
Modern Desktop Managed Workload Staging – Device Configuration
Modern Desktop Managed Workload Staging – Endpoint Protection
Modern Desktop Managed Workload Staging – Resource access policies
Modern Desktop Managed Workload Staging – Client Apps
Modern Desktop Managed Workload Staging – Office Click-to-Run apps
Modern Desktop Managed Workload Staging – Windows Update Policies
Your result should look like this:
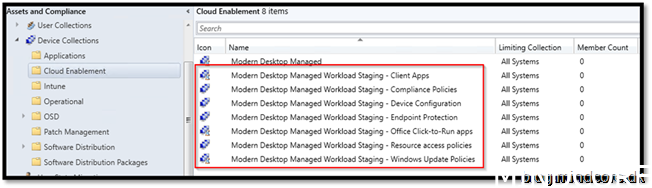
With this setup we can add devices to the workloads we need to test.
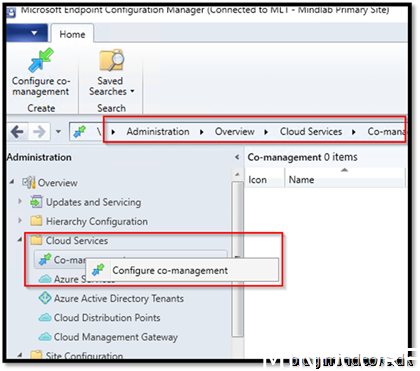
Go to AdministrationOverviewCloud ServicesCo-management
Configure co-management
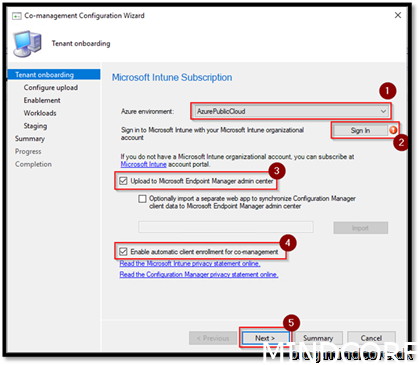

Sign in using a global admin
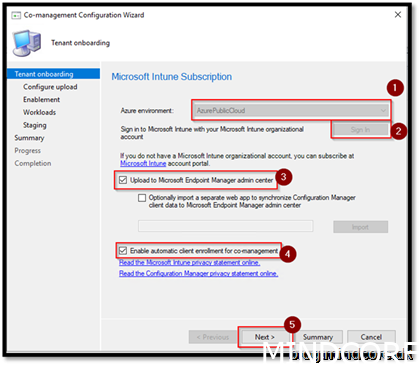
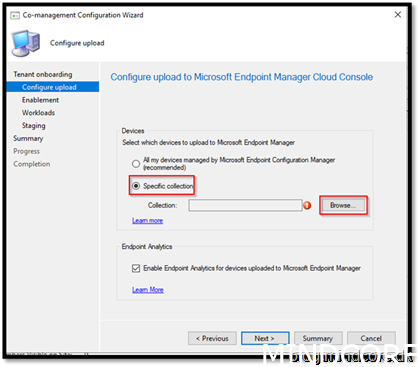
For the tenant attach part we will only upload the devices that also will be co-managed. Most designs you would just upload all devices as nothing happens on the client side. It is all backend stuff. Be aware though a good RBAC model should be in place.
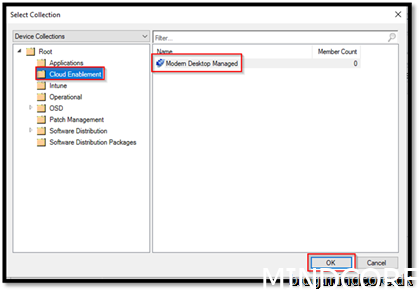
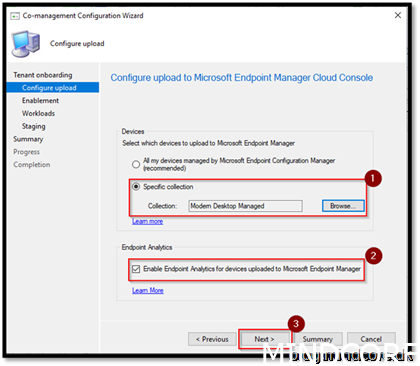
When we add a device to the collection “Modern Desktop Managed” our device will be manageable from admin center and the tenant attach feature will be in place.
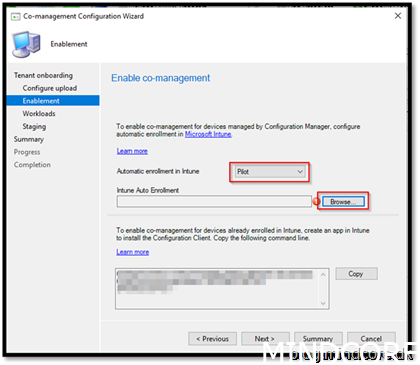
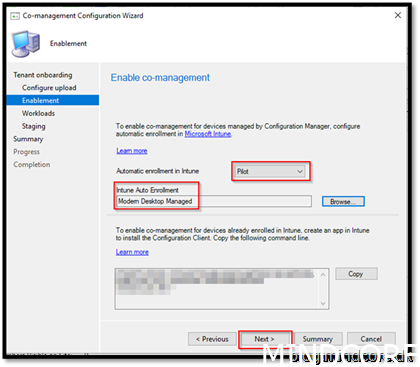
For our devices going co-managed, first always use “Pilot”
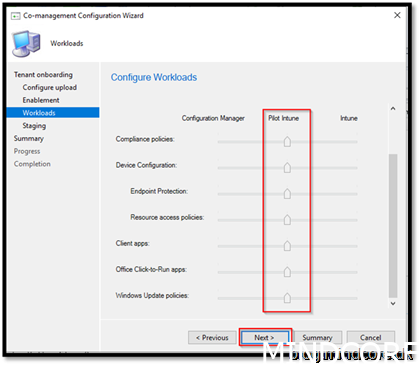
Adding all the workloads as pilot will make the whole setup more agile. Even we are not doing pilot on every workload at the same time, it will be easy to setup it up once and leave it.
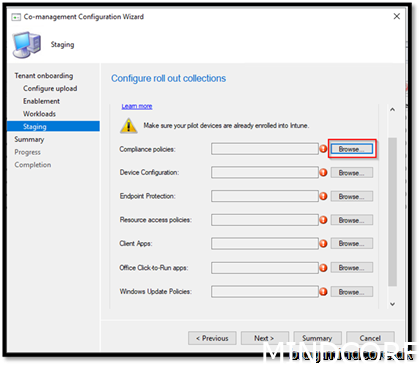
Browse for the collections created earlier and add them to each workload.
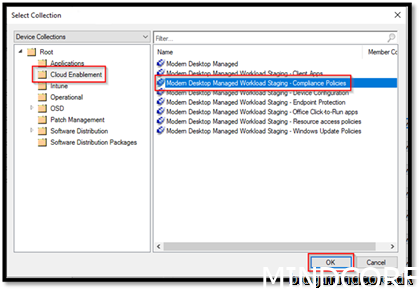
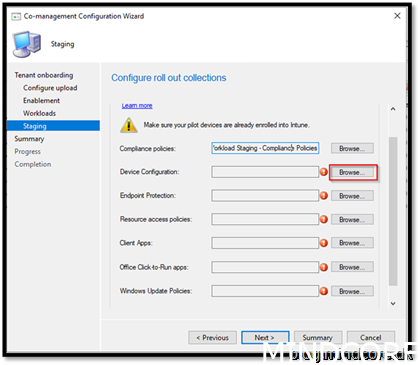
Same procedure for every workload
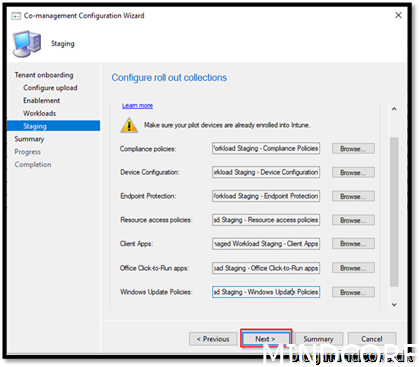
And we are ready to finalize the wizard
Next
Close
You should end up with a result like this:
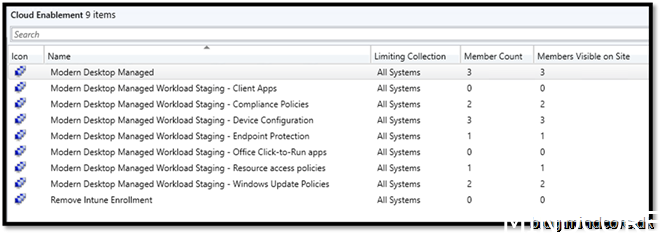
And here you add a device and move it around as you need to do your testing on the different workloads.
Here you can see what each workload will do for you:
|
Workload
|
Description |
|
Compliance policies |
Rules and settings that a device must comply with to be considered compliant by conditional access |
|
Device configuration |
Device configuration are settings managed for devices in the SCCM console in the Compliance Settings tab. Moving this tab will also move Endpoint Protection and Resource access policies. Without moving this no Configuration profiles in Intune will be applied on the client running co-management. |
|
Endpoint Protection |
Includes: Antimalware Policies Windows Defender Firewall Policies Windows Defender SmartScreen Windows Encryption Windows Defender Exploit Guard Windows Defender Application Guard Windows Defender Application Control Moving this will not overwrite existing policies applied before a given profile has been applied. This is to secure a baseline security profile. |
|
Resource access policies |
Includes: Certificate Profiles Email Profiles VPN Profiles Wi-Fi Profiles Windows Hello for Business profiles |
|
Client apps |
Enables Intune to manage client apps and PowerShell Scripts. Required SCCM packages will still be applied when the SCCM client is installed |
|
Office Click-to-Run apps |
Microsoft 365 App installation |
|
Windows Update policies |
Quality, drivers, and feature updates |
While configuring co-managed devices by using Configuration Manager and Intune, there is a limitation where feature update policies may not immediately take effect. This limitation causes devices to update to a later feature update than the one that’s configured in Intune. This limitation will be removed in a future update to Configuration Manager. This can be achieved in 2 ways.
GPO or OMA-URI
GPO
Computer configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows Update -> Windows Update for Business
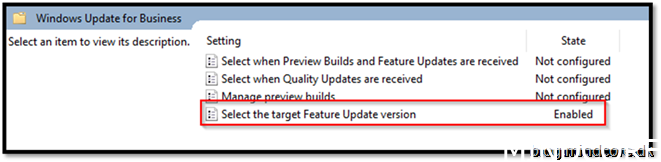
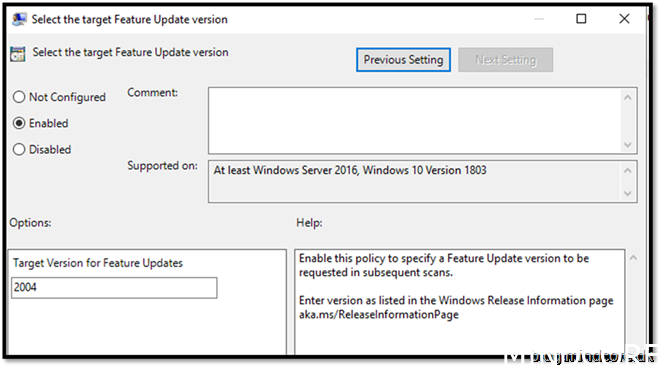
Assign the policy to your devices that are going to be migrated to co-managed devices + WUfB.
OMA-URI
https://endpoint.microsoft.com
Devices -> Windows -> Configuration profiles -> create profile
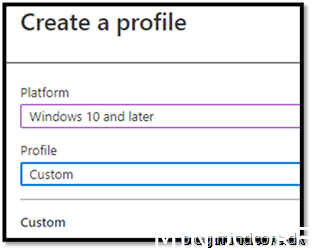
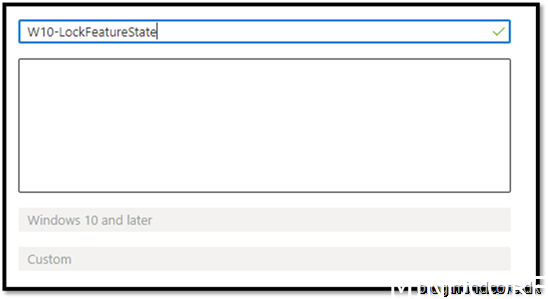
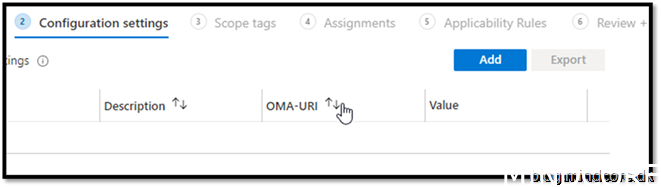
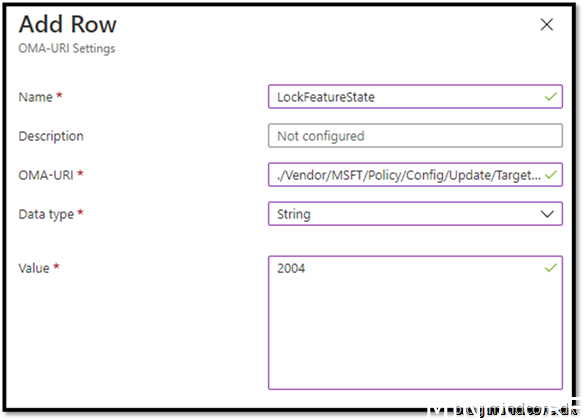
Assign it to your device group where your co-managed devices will go.
To verify the policy has been added, go to the registry on a client where the policy applies.
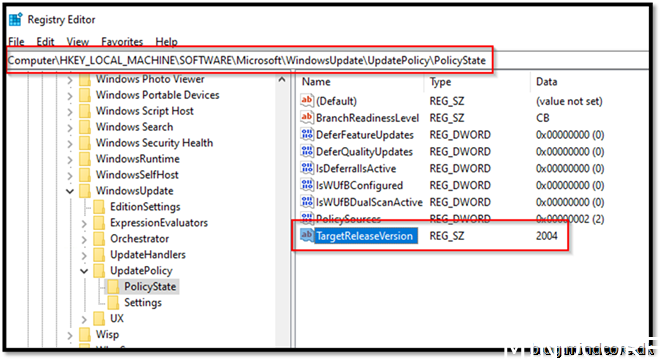
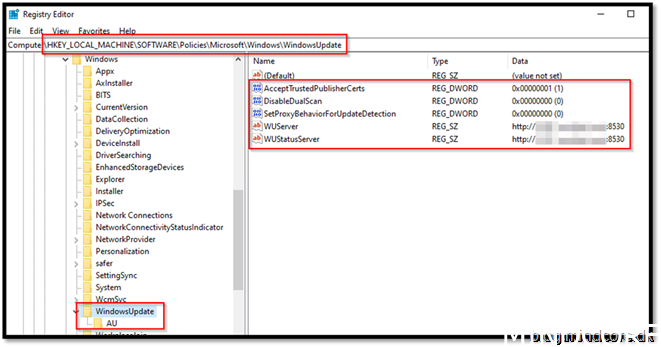
Your configuration manager managed device will still have Windows update registry applied to be able to leverage 3rd party patches and Microsoft 365 apps patches.
Before moving workload to WUfB we need to setup a Windows 10 ring in the MEMAC and we should also add a feature block mirroring what we did in the policy.
Open the admin center https://endpoint.microsoft.com/
Go to devices -> Windows 10 update rings -> Create profile
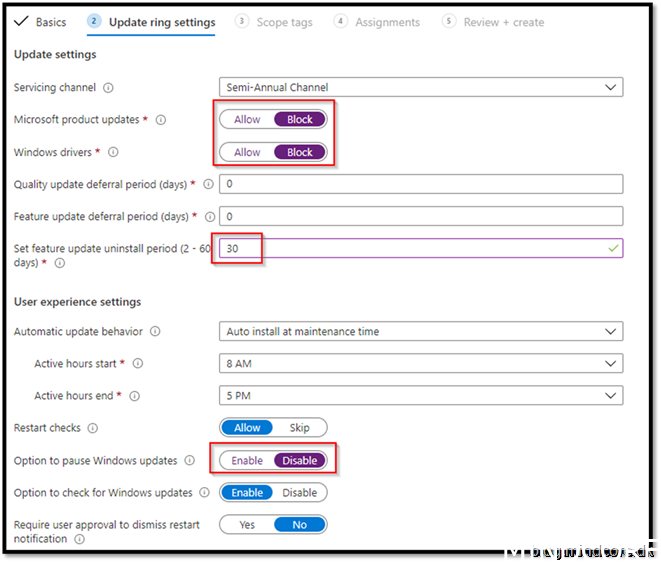
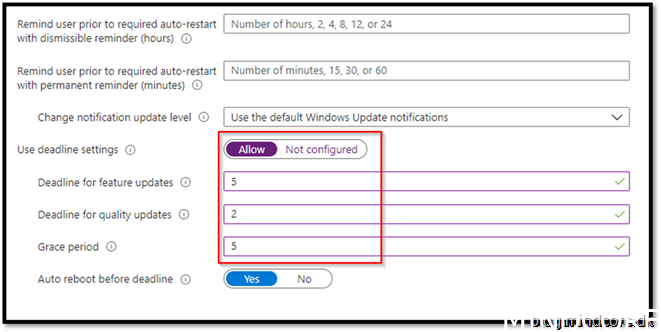
I leave most of the settings as standard as possible.
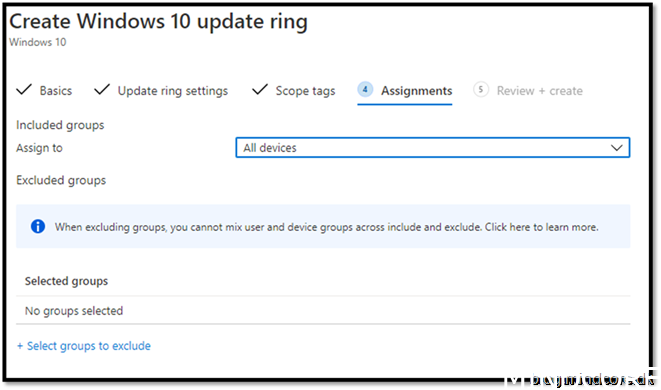
Create it.
We also need a feature hold.
Open the admin center https://endpoint.microsoft.com/
Go to devices -> Windows 10 feature updates -> Create profile
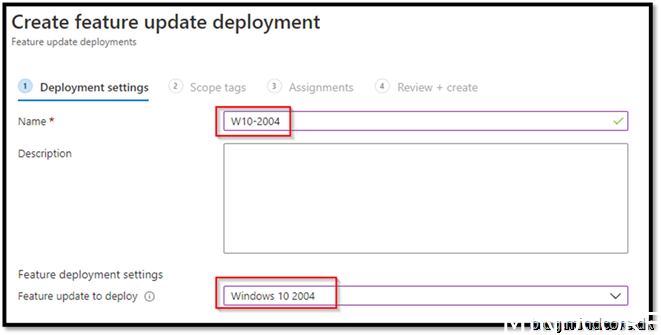
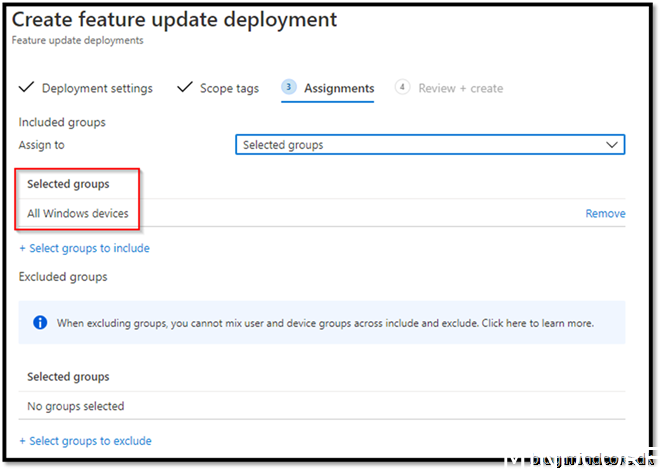
This particular policy cannot be deployed to all devices, or at least the option is not there, so we just need to make a Windows device group which contains the devices we need to manage.
It can be done in several ways, but I will not cover that it this post.
Create it.
Finally, we can move the workload on our test clients to see the effect of Windows Update for Business. Just add the clients to the collections where the workload applies. Simple and easy!
For more content how to be clear of what each setting do in your windows 10 ring, please see this 34 minutes video with Aria Carley and Dune Desormeaux.
How the client reacts
Windows Quality update – From Microsoft directly and with the build-in notification in Windows 10.
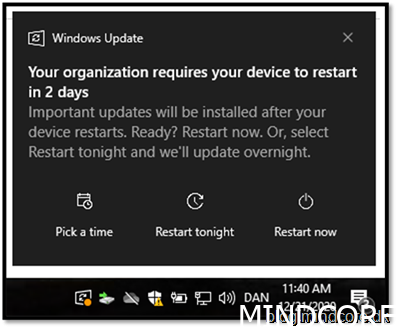
MEMAC – Windows update Ring
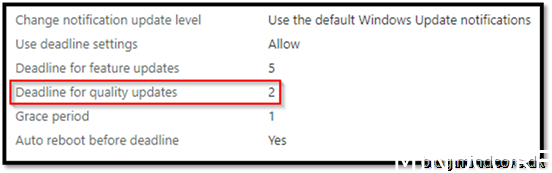
As you may notice my windows client will reboot in 2 days, which is set in the update ring. That means the client honor the policy set from MEM and proof that the update did not come from Configuration Manager.

Windows feature update – From Microsoft directly and with the build-in notification in Windows 10.
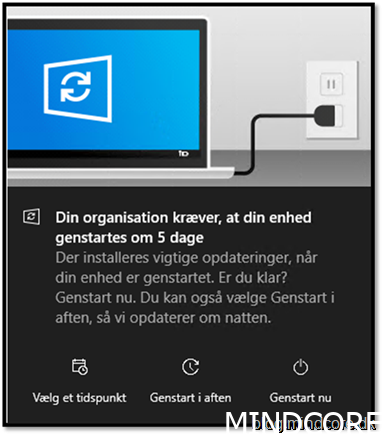
(Picture in danish sorry about that.)
MEMAC – Windows update Ring
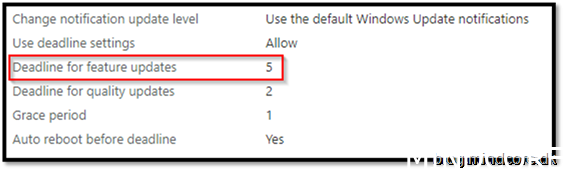
As before with quality updates, Feature updates also have a deadline, but I have configured that to be a little longer to give end user a chance as it takes more time to reboot while updating the feature versus a quality update.
To test third party updates are working, I added Management engines 3rd party management package to patch google chrome. How to integrate that is not covered and not part of what we are achieving in this blog post.
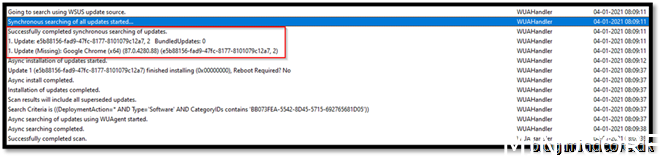
As you can see the result of using WUAHandler.log that Chrome has been patched on my client.
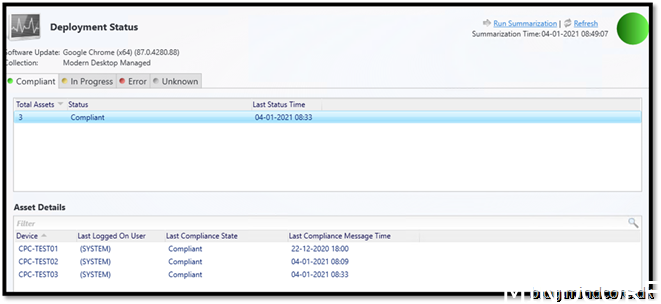
Dual scan magic, having both updates from Microsoft and managing other portions from Configuration Manager.
From Configuration Manager monitor we see that all clients have received the patch and are compliant
And the proof that Office 365 patches goes through configuration manager can be verified by looking into the configuration manager console that we have clients asking for updates:
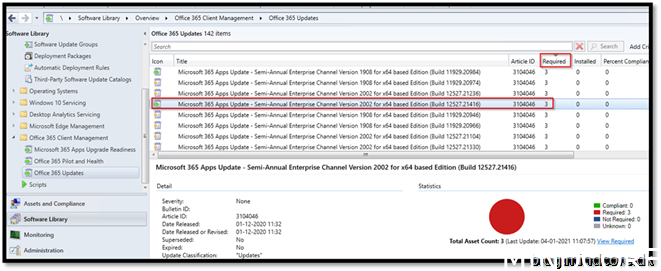
And the client receiving the update from Configuration Manager.
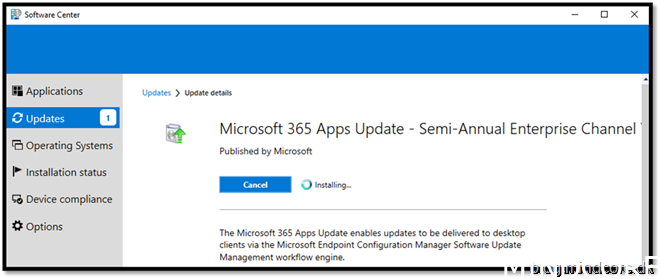
Job done and we are happy!
Summary
As we work more and more from home, we have more use for technology that helps us managing our devices. To make a transition we can do that in small steps ensuring that the business will continue to be productive while adopting the new patch strategy.
- Setup your configuration manager environment to meet the requirements
- Configure Intune with Windows update ring
- Setup a policy to prevent windows feature update from happening while transitioning to modern
- Test that it works as intended in a small group of devices and then roll out in a ring rollout strategy.
Happy testing!
Mattias Melkersen is a community driven and passionate modern workplace consultant with 20 years’ experience in automating software, driving adoption and technology change within the Enterprise. He lives in Denmark and works at Mindcore.
He is an Enterprise Mobility Intune MVP, Official Contributor in a LinkedIn group with 41.000 members and Microsoft 365 Enterprise Administrator Expert.
Mattias blogs, gives interview and creates a YouTube content on the channel "MSEndpointMgr" where he creates helpful content in the MEM area and interview MVP’s who showcase certain technology or topic.
Official Contributor here "Modern Endpoint Management":
https://www.linkedin.com/groups/8761296/














